So, is the brain a muscle? Our lives seem less of a struggle if some things are under our control. It’s easier if we know how to do certain things and achieve specific objectives. Unlike us, our brain is one such part of our body that controls every other part of our body.
When the brain is such a vital part of the body, it’s essential to understand its nature, functioning, and anatomy. So the question comes- Is the brain a muscle?
This article will tell you what the brain is and how it can be considered a muscle OR an organ based on brain function. Does the brain need physical exercise like our body to stay fit and healthy, or are there other ways to keep it fit? We will answer all these questions here to make you nerdBRAIN!
Is Your Brain a Muscle or Organ?
One of the reasons the notion of the brain being a muscle is talked about could be the phrases like ‘work your brain’ or ‘brain exercise.’ These terms provide the assumption that because the brain needs exercise, it’s a muscle, but the same is not entirely true (though physical exercise could be helpful for your cognitive functions).
So to make it clear, the brain is an ORGAN and not a muscle. As mentioned earlier, the brain controls every aspect of the human body – from motor skills to involuntary activities like digesting food. Motions to emotions, everything is worked up by the human brain. You can’t call the brain can’t a muscle because a muscle cannot perform these complex activities.
Talking about the constitution of a muscle and a brain – Muscle consists of muscle tissue, and these tissues form when the muscle cells group. This bundle of tissues helps in the contraction and relaxation of muscles (produces motion or/and force).
Being the fattiest organ, the brain consists of neurons, glial cells (supporting cells), grey matter, and white matter (soft tissues). You can find Neurons (nerve cells) and Glial cells in grey and white matter. The role of neurons is to send and receive electrical and chemical signals from different body parts.
Grey matter is a neural tissue you find in the cerebral cortex, the brain nuclei, and the basal ganglia. White matter contains axons which are extensions of neurons. The cerebrospinal fluid inside which the brain floats protects the brain. These constituents make the brain a complex organ.
How Is the Brain Working Like a Muscle?
So you already know that the brain is not a muscle. A part of the brain, i.e., muscle tissues (formed by smooth muscle cells), forms a cellular structure (middle layer) for the brain’s blood flow and maintain the brain’s blood pressure. In some ways, we can say that, like muscles, the brain also needs some mental stimulation to make it stronger and more flexible.
When we say ‘exercise your brain,’ it needn’t always mean physical activity, but how to achieve brain fitness and improve the thinking process and the cognitive function through problem-solving, brain training games, and proper nutrition.
Solving challenging puzzles and tackling difficult problems in games can increase working memory and improve brain health and cognitive skills. Evidence shows that these activities are great exercises, especially for growing children and young adults, as they can help them develop reasoning, improve memory, and make performing daily tasks easier.
Apart from games and puzzles, certain artistic activities can also help improve cognitive skills. It can also slow down the brain aging process that brings various neurological conditions like dementia and Alzheimer’s disease and keeps the brain healthy.
Is the Brain a Voluntary or Involuntary Muscle?
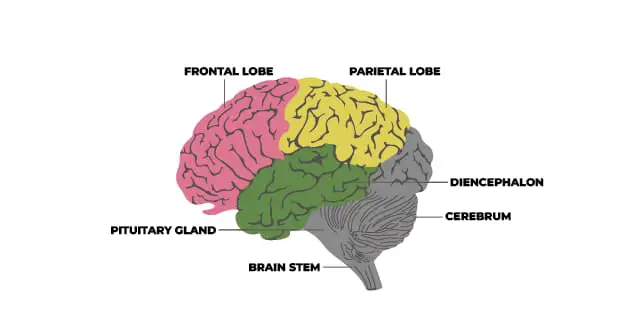
Since the brain can’t be considered a muscle, the idea of voluntary and involuntary doesn’t come into the picture. You can discuss brain anatomy here, which will make you understand how different parts of the brain function to perform bodily functions.
Brain Stem
You find it at the base of the brain, which then connects to the spinal cord. The brain stem helps regulate heart rate and breathing and aids in digestion (involuntary activities).
Cerebrum
This part of the brain is divided into two hemispheres, and each of these hemispheres is further divided into four parts called lobes. Lobes with their functions are mentioned below:
- Frontal lobe
This region regulates higher executive functions like reasoning, problem-solving, emotions, and feelings.
- Parietal lobe
This region is responsible for regulating sensory information like touch, pain, pressure, etc.
- Temporal lobe
This region processes activities like forming memories, recognizing languages, and sensory information related to hearing.
- Occipital lobe
This region deals with visual information and secondary areas like identifying objects, distance, and depth.
Pituitary Gland
We find this gland attached to the hypothalamus, and it controls the activities of the hormone-secreting glands. This gland plays an essential role during reproduction, puberty, and the growth of the human body and human brain.
Cerebellum
Motor skills and coordination is taken care of by this part of the brain, and it helps in maintaining balance and posture of the body.
Diencephalon
This part is found at the base of the brain and consists of three parts- the thalamus, epithalamus, and hypothalamus.
Thalamus regulates consciousness, sleep, and memory.
Epithalamus deals with basic moods, drives, and emotions in the human body.
Hypothalamus regulates apatite, the release of hormones, body temperature, and sleep cycle.
How Does the Brain Get Stronger When It Takes On Challenges?

Learning new things and exercising through various activities can make your brain more efficient and flexible to learn, analyze and strategize more. In this way, the brain is like a muscle because muscles get stronger and larger with exercise.
So if a person lifts 30 pounds, he can go on to lift 90 pounds after working out for a while. Similar is the case with the brain; it gets stronger with usage.
Let’s talk about what happens inside your brain when you solve a challenging task. The neurons in your brain start connecting in a complicated network, and these communications between the neurons make you solve the task.
When we learn new things, these connections become stronger and multiply. Thus, the more we learn and solve, the more the cells would multiply and make connections. So the result would be you solving your problem plus coming out with a stronger and smarter brain!
Evidence shows that an enriched environment helps better brain activity, so interacting with different groups of people with different ideologies and interaction with the outside world can make you smarter and more able to solve problems and learn new things.
We can take the example of babies. How they come into this world unaware of any social constructs and any interactions, but somehow every one of them learns how to speak their local languages and learn etiquettes, morals, and values that they perceive in the outside environment.
This happens because babies continuously live within their social environment and listen to every voice and word. They attempt to mimic those voices, which later become words and then converse in complete sentences.
Studies have shown that even animals who interact with their mates lead to the development of their brains. There are enough examples around us to realize how strong our brain is and how we can make it stronger.
Final Words – Is the Brain a Muscle?
Though it may seem hard to understand the brain’s capabilities, it’s comparatively easier to make your brain learn new things and challenge it every once in a while to keep your brain young, irrespective of your age.
Our brain plays a huge role in everything that our body conceives, learns, and performs, so working up our brain should be the most important part of our exercise routine because a healthy brain provides a healthy body and mind. Stick to a good brain training game and play it regularly.
Therefore, even though the brain cannot be considered a muscle, that doesn’t mean you are not supposed to look after it. As mentioned above, our brain needs to be taken care of not only for better development but also so that the possibility of neurological disorders as we enter old age can decrease.
